File类的使用
File类的一个对象,代表一个文件或一个文件目录(俗称:文件夹)
File类声明在java.io包下。
File类中涉及到关于文件或文件目录的创建、删除、重命名、修改时间、文件大小等方法。
并未涉及到写入或读取文件内容的操作,如果需要读取或写入文件内容,必须使用IO流来完成。
后续File类的对象常会作为参数传递到流的构造器中,指明读取或写入的”终点”。
Demo
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 public class FileTest @Test public void test1 () File file1 = new File("hello.txt" ); File file2 = new File("D:\\workspace_idea1\\JavaSenior\\day08\\he.txt" ); System.out.println(file1); System.out.println(file2); File file3 = new File("D:\\workspace_idea1" ,"JavaSenior" ); System.out.println(file3); File file4 = new File(file3,"hi.txt" ); System.out.println(file4); } @Test public void test2 () File file1 = new File("hello.txt" ); File file2 = new File("d:\\io\\hi.txt" ); System.out.println(file1.getAbsolutePath()); System.out.println(file1.getPath()); System.out.println(file1.getName()); System.out.println(file1.getParent()); System.out.println(file1.length()); System.out.println(new Date(file1.lastModified())); System.out.println(); System.out.println(file2.getAbsolutePath()); System.out.println(file2.getPath()); System.out.println(file2.getName()); System.out.println(file2.getParent()); System.out.println(file2.length()); System.out.println(file2.lastModified()); } @Test public void test3 () File file = new File("D:\\workspace_idea1\\JavaSenior" ); String[] list = file.list(); for (String s : list){ System.out.println(s); } System.out.println(); File[] files = file.listFiles(); for (File f : files){ System.out.println(f); } @Test public void test4 () File file1 = new File("hello.txt" ); File file2 = new File("D:\\io\\hi.txt" ); boolean renameTo = file2.renameTo(file1); System.out.println(renameTo); } @Test public void test5 () File file1 = new File("hello.txt" ); file1 = new File("hello1.txt" ); System.out.println(file1.isDirectory()); System.out.println(file1.isFile()); System.out.println(file1.exists()); System.out.println(file1.canRead()); System.out.println(file1.canWrite()); System.out.println(file1.isHidden()); System.out.println(); File file2 = new File("d:\\io" ); file2 = new File("d:\\io1" ); System.out.println(file2.isDirectory()); System.out.println(file2.isFile()); System.out.println(file2.exists()); System.out.println(file2.canRead()); System.out.println(file2.canWrite()); System.out.println(file2.isHidden()); } @Test public void test6 () throws IOException File file1 = new File("hi.txt" ); if (!file1.exists()){ file1.createNewFile(); System.out.println("创建成功" ); }else { file1.delete(); System.out.println("删除成功" ); } } @Test public void test7 () File file1 = new File("d:\\io\\io1\\io3" ); boolean mkdir = file1.mkdir(); if (mkdir){ System.out.println("创建成功1" ); } File file2 = new File("d:\\io\\io1\\io4" ); boolean mkdir1 = file2.mkdirs(); if (mkdir1){ System.out.println("创建成功2" ); } File file3 = new File("D:\\io\\io1\\io4" ); file3 = new File("D:\\io\\io1" ); System.out.println(file3.delete()); } }
流的分类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 一、流的分类: 1.操作数据单位:字节流、字符流 2.数据的流向:输入流、输出流 3.流的角色:节点流、处理流 二、流的体系结构 抽象基类 节点流(或文件流) 缓冲流(处理流的一种) InputStream FileInputStream (read(byte[] buffer)) BufferedInputStream (read(byte[] buffer)) OutputStream FileOutputStream (write(byte[] buffer,0,len) BufferedOutputStream (write(byte[]buffer,0,len) / flush() Reader FileReader (read(char[] cbuf)) BufferedReader (read(char[] cbuf) / readLine()) Writer FileWriter (write(char[] cbuf,0,len) BufferedWriter (write(char[] cbuf,0,len) / flush()
字节流与字符流的区别:
FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream 可以完成所有格式文件的赋值。
FileReader 和 FileWriter 只可以完成文本文件的复制,却无法完成视频格式文件的复制。
因为字节是不需要解码和编码的,将字节转化为字符才存在解码和编码的问题。
字节流可以从所有格式的设备中读写数据,但字符流只能从文本格式的设备中读写数据。
Demo
处理文本文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 import java.io.*;public class TestIO public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { FileReader fr = new FileReader("C:\\Users\\DELL\\Desktop\\TestIO.java" ); int ch; int cnt = 0 ; ch = fr.read(); while (-1 != ch) { ++cnt; System.out.printf("%c" , (char )ch); ch = fr.read(); } System.out.printf("该文件字符的个数是:%d\n" , cnt); fr.close(); } } -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- import java.io.*;public class TestIO_2 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { FileInputStream fr = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\DELL\\Desktop\\TestIO.java" ); int ch; int cnt = 0 ; ch = fr.read(); while (-1 != ch) { ++cnt; System.out.printf("%c" , (char )ch); ch = fr.read(); } System.out.printf("该文件字符的个数是:%d\n" , cnt); fr.close(); } }
处理非文本文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 import java.io.*;public class TestFileReaderWriterCopy public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { FileReader fr = new FileReader("D:\\share\\S5\\di-20 流\\TestFileReaderWriterCopy.java" ); FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("d:/zhangsan.haha" ); int ch; ch = fr.read(); while (-1 != ch) { fw.write(ch); ch = fr.read(); } fw.flush(); fr.close(); fw.close(); } } ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- import java.io.*;public class TestFileReaderWriterCopy_2 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { FileReader fr = new FileReader("E:\\IBM教学\\java\\lesson_io\\柯南.mp3" ); FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("d:/xiuyi.xixi" ); int ch; ch = fr.read(); while (-1 != ch) { fw.write(ch); ch = fr.read(); } fw.flush(); fr.close(); fw.close(); } }
File Reader Writer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 public class FileReaderWriterTest public static void main (String[] args) File file = new File("hello.txt" ); System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath()); File file1 = new File("day09\\hello.txt" ); System.out.println(file1.getAbsolutePath()); } @Test public void testFileReader () FileReader fr = null ; try { File file = new File("hello.txt" ); fr = new FileReader(file); int data; while ((data = fr.read()) != -1 ){ System.out.print((char )data); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (fr != null ){ try { fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } @Test public void testFileReader1 () FileReader fr = null ; try { File file = new File("hello.txt" ); fr = new FileReader(file); char [] cbuf = new char [5 ]; int len; while ((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1 ){ String str = new String(cbuf,0 ,len); System.out.print(str); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (fr != null ){ try { fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } @Test public void testFileWriter () FileWriter fw = null ; try { File file = new File("hello1.txt" ); fw = new FileWriter(file,false ); fw.write("I have a dream!\n" ); fw.write("you need to have a dream!" ); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (fw != null ){ try { fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } @Test public void testFileReaderFileWriter () FileReader fr = null ; FileWriter fw = null ; try { File srcFile = new File("hello.txt" ); File destFile = new File("hello2.txt" ); fr = new FileReader(srcFile); fw = new FileWriter(destFile); char [] cbuf = new char [5 ]; int len; while ((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1 ){ fw.write(cbuf,0 ,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (fw != null ) fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if (fr != null ) fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
缓冲流
缓冲流就是带有缓冲区的输入输出流
缓冲流可以i显著的减少我们对IO访问的次数,保护我们的硬盘!
缓冲流本身就是处理流(处理流也称包裹流),缓冲流必须要依附于节点流(节点流也称原始流)
处理流是包裹在原始节点流上的流,相当于包括在管道上的管道!
包裹流
我们只有
BufferedInputStream
BufferedOutputStream类
BufferedWriter
BufferedReader
没有
BufferedStream
BufferedFileInputStream(但有FileInputStream)
BufferedFileOutoutStream(但有FileOutputStream)
BufferedFileReader(但有FileReader)
BufferedFileWriter(但有FileWriter)
所以四个流都是包裹流。
BufferReader 和 BufferWriter
Reader FileReader InputStream FileInputStream
BufferedInputStream 流中都没有 readLine 方法
DataInputStream 流中有 readLine 方法,但已经被标记为过时。
BufferedReader 流中有 readLine 方法,并且该方法是可以正确使用的。
BufferedReader 流中有 readLine 是个非常有用的方法,BufferedReader 是要经常使用的流
利用BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter 可以提高读写文本文件内容的速度。
完成非文本文件的copy
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 import java.io.*;public class TestInputStreamOutputStreamCopy public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { FileInputStream fr = new FileInputStream("E:\\IBM教学\\java\\lesson_io\\柯南.mp3" ); FileOutputStream fw = new FileOutputStream("d:/xiuyi.xixi" ); int ch; ch = fr.read(); while (-1 != ch) { fw.write(ch); ch = fr.read(); } fw.flush(); fr.close(); fw.close(); } } --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- import java.io.*;public class TestInputStreamOutputStreamCopy_2 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { FileInputStream fr = new FileInputStream("C:\\1.jpg" ); FileOutputStream fw = new FileOutputStream("d:/xiuyi.xixi" ); int ch; ch = fr.read(); while (-1 != ch) { fw.write(ch); ch = fr.read(); } fw.flush(); fr.close(); fw.close(); } } --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- import java.io.*;public class TestInputStreamOutputStreamCopy_3 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream("E:\\IBM教学\\java\\lesson_io\\柯南.mp3" )); BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d:/xiuyi.xixi" )); byte [] buf = new byte [1024 ]; int len; len = bis.read(buf); while (-1 != len) { bos.write(buf, 0 , len); len = bis.read(buf); } bos.flush(); bos.close(); bis.close(); } }
利用 BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter 完成文本文件的复制
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 import java.io.*;public class TestBufferedReaderWriterCopy public static void main (String[] args) { BufferedReader br = null ; BufferedWriter bw = null ; try { br = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("D:\\share\\S5\\di-20 流\\TestBufferedReaderWriterCopy.java" ) ); bw = new BufferedWriter( new FileWriter("d:/share/Writer.txt" ) ); String str = null ; while (null != (str=br.readLine())) { bw.write(str); bw.newLine(); } bw.flush(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(-1 ); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(-1 ); } finally { try { bw.close(); br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(-1 ); } } } }
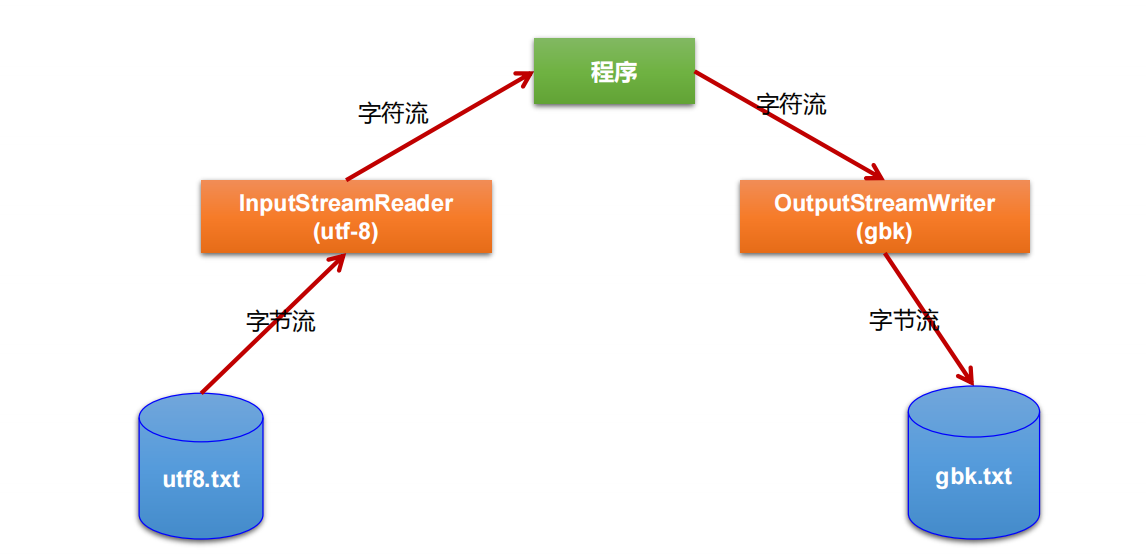
转换流
转换流提供了在字节流和字符流之间的转换
javaAPI提供了两个转换流:
InputStreamReader:将InputStream转换为Reader。
OutputStreamWriter:将Writer转换为OutputStream。
字节流中的数据都是字符时,转成字符流操作更高效。
很多时候我们使用转换流来处理文件乱码问题。实现编码和解码的功能。
Demo
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 public class InputStreamReaderTest @Test public void test1 () throws IOException FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("dbcp.txt" ); InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"UTF-8" ); char [] cbuf = new char [20 ]; int len; while ((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1 ){ String str = new String(cbuf,0 ,len); System.out.print(str); } isr.close(); } @Test public void test2 () throws Exception File file1 = new File("dbcp.txt" ); File file2 = new File("dbcp_gbk.txt" ); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2); InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"utf-8" ); OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"gbk" ); char [] cbuf = new char [20 ]; int len; while ((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1 ){ osw.write(cbuf,0 ,len); } isr.close(); osw.close(); } } -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- import java.io.*;public class TestStringInput public static void main (String[] args) { String str = null ; BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader ( new InputStreamReader(System.in) ); try { str = br.readLine(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(-1 ); } System.out.println("str = " + str); try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(-1 ); } } }
其它流 Demo
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 public class OtherStreamTest public static void main (String[] args) BufferedReader br = null ; try { InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in); br = new BufferedReader(isr); while (true ) { System.out.println("请输入字符串:" ); String data = br.readLine(); if ("e" .equalsIgnoreCase(data) || "exit" .equalsIgnoreCase(data)) { System.out.println("程序结束" ); break ; } String upperCase = data.toUpperCase(); System.out.println(upperCase); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (br != null ) { try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } @Test public void test2 () PrintStream ps = null ; try { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("D:\\IO\\text.txt" )); ps = new PrintStream(fos, true ); if (ps != null ) { System.setOut(ps); } for (int i = 0 ; i <= 255 ; i++) { System.out.print((char ) i); if (i % 50 == 0 ) { System.out.println(); } } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (ps != null ) { ps.close(); } } } @Test public void test3 () throws IOException DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("data.txt" )); dos.writeUTF("刘建辰" ); dos.flush(); dos.writeInt(23 ); dos.flush(); dos.writeBoolean(true ); dos.flush(); dos.close(); } @Test public void test4 () throws IOException DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("data.txt" )); String name = dis.readUTF(); int age = dis.readInt(); boolean isMale = dis.readBoolean(); System.out.println("name = " + name); System.out.println("age = " + age); System.out.println("isMale = " + isMale); dis.close(); } }
ReadLine与回车符 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 import java.io.*;public class TestBuffered public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception String str = "zhangsan" ; System.out.println("str = " + str); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); str = br.readLine(); System.out.println("------------" ); System.out.println(str + "123" ); System.out.println(str.equals("" )); System.out.println(str == null ); } }
对象的序列化
所序列化是指:把一个Object对象直接转换为字节流,然后把这个字节流直接写入本地硬盘或网络中。
如果要想把某个对象序列化,则必须实现Serializable接口。
Serializable 接口中并没有任何方法,该接口被称为标记接口,如果一个类实现了 Seralizable 接口,潜在含义就是告诉编译器这个类是允许被序列化的,如果程序中存在序列化该对象的Code,编译器就会自动进行相应的处理已完成该对象的序列化,如果该对象没有实现Serializable接口,程序中却存在该对象被序列化的代码,编译器编译是会报错。
在java中 transient 修饰的成员变量在对象序列化时不被序列化。
Demo
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 import java.io.*;public class TestObjectIO public static void main (String[] args) { ObjectOutputStream oos = null ; ObjectInputStream ois = null ; Student ss = new Student("zhansan" , 1000 , 88.8f ); Student ss2 = null ; try { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d:/share/java/ObjectOut.txt" ); oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos); oos.writeObject(ss); ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("d:/share/java/ObjectOut.txt" )); ss2 = (Student)ois.readObject(); System.out.println("ss2.sname = " + ss2.sname); System.out.println("ss2.sid = " + ss2.sid); System.out.println("ss2.sscore = " + ss2.sscore); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("文件没有找到!" ); System.exit(-1 ); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(-1 ); } finally { try { oos.close(); ois.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(-1 ); } } } } class Student implements Serializable //如果将implements Serializable 注释掉,则程序编译时就会报错 Serializable 是空接口,起标识作用。 public String sname = null ; public int sid = 0 ; transient public float sscore = 0 ; public Student (String name, int id, float score) { this .sname = name; this .sid = id; this .sscore = score; } }
Print流与Object流 Print流:
Print流只有输出,没有输入
分类
PrintWriter 输出字符
PrintStream 输出字节
Print流的由来:
Writer 的 writer 方法可以写入
一个字符
一个字符数组
一个字符数组一部分
一个字符串
一个字符的一部分
OutputStream 的writer 方法可以写入:
DataOutputStream 流可以写入:
一个字节
一个字节数组(继承自OutputStream)
一个字节数组的一部分
所有的基本类型数据的二进制代码
如writerDouble(8.8);写入的是8.8的二进制代码,共占8个字节。
PrintStream 流的print可以写入:
所有基本类型数据的字符串形式表示:
如print(8.8);写入的是’8’’.’’8’这三个字符,共占3个字节。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import java.io.*;public class TestPrintStream_1 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d:/share/kk.txt" )); dos.writeLong(12345 ); dos.close(); System.out.printf("%#X\n" , 12345 ); PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("d:/share/kk2.txt" ), true ); ps.println(12345 ); ps.close(); } }
标准输入输出的重定向
编程实现将键盘输入到的数据输入A文件中,如果输入有误,则把出错信息输入到B文件中。
Demo
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 import java.io.*;import java.util.*;public class TestSetOutErr public static void main (String[] args) { PrintStream psOut = null ; PrintStream psError = null ; Scanner sc = null ; try { psOut = new PrintStream("d:/Out.txt" ); psError = new PrintStream("d:/error.txt" ); sc = new Scanner(System.in); int num; System.setOut(psOut); System.setErr(psError); while (true ) { num = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println(num); } } catch (Exception e) { System.err.println("出错的信息是:" ); e.printStackTrace(); } } } ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- import java.io.*;public class TestSys public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("d:/heihei.asd" ); System.setOut(ps); System.out.println("哈哈" ); } } ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- import java.io.*;public class TestSetSystemOut public static void main (String[] args) { PrintStream ps_out = null ; try { ps_out = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("d:/share/ww.txt" )); System.setOut(ps_out); System.out.println(12 ); System.out.println(55.5 ); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { ps_out.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }